Introduction Financial Definitions
Fixed Cost:
- A cost of a business expense that doesn't change even when there's an increase or decrease in the number of goods and services produced or sold.
- Fixed Costs are expenses that have to be paid by a company, independent of any business activity
- Fixed costs are allocated in the indirect expense section of the income statement which leads to operating profit.
- Depreciation is one common fixed cost that is recorded as an indirect expense.
Variable Cost:
- A variable cost is a corporate expense that changes in proportion to how much a company produces or sells.
- Variable costs are usually viewed as short-term costs as they can be adjusted quickly.
- The variable cost of production is a constant amount per unit produced.
- Variable costs increase or decrease depending on a company's production or sales volume—they rise as production increases and fall as production decreases.
- Total Variable Cost = Total Quantity of Output X Variable Cost Per Unit of Output
Sales Price:
The sales price is the price at which a certain class of goods or services is typically sold
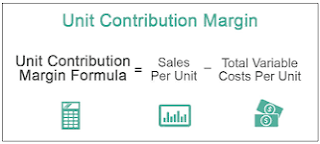
Unit Margin:
- Unit margin is also called Unit Contribution Margin
- Unit margin can be stated on a gross or per-unit basis
- Unit Margin is the amount of the product selling price over and above the variable cost per unit
Total Margin:
Total Margin is the total amount of margin or profit made after deducting fixed costs
Ceteris Paribus
- Ceteris paribus is translated into English as "all else being equal."
- It is a Latin phrase that literally "holding other things constant,"
- ceteris paribus is often used when making arguments about cause and effect
- It acts as a shorthand indication of the effect one economic variable has on another, provided all other variables remain the same.
- Many economists rely on ceteris paribus to describe relative tendencies in markets and to build and test economic models.
Unfavorable Variance
- An unfavorable variance is an accounting term that describes instances where actual costs are greater than the standard or projected costs.
- What Is Unfavorable Variance?
- An unfavorable variance is an accounting term that describes instances where actual costs are greater than the standard or projected costs.
- The sooner an unfavorable variance is detected, the sooner attention can be directed toward fixing any problems
- The unfavorable variance could be the result of lower revenue, higher expenses, or a combination of both.
Favorable Variances
- A favorable variance is where actual income is more than budget, or actual expenditure is less than budget.
- This is the same as a surplus where expenditure is less than the available income.
- Favorable variances related to price are only derived from the difference between actual and expected prices paid, and so have no bearing at all on the underlying efficiency of a company's operations.
- Obtaining a favorable variance does not necessarily mean much, since it is based upon a budgeted or standard amount that may not be an indicator of good performance
Positive Correlation
- A positive correlation is a relationship between two variables that tend to move in the same direction.
- A positive correlation exists when one variable tends to decrease as the other variable decreases, or one variable tends to increase when the other increases.
- In finance, correlations are used to describe how individual stocks move with respect to the wider market.
- Beta is a common measure of market correlation, usually using the S&P 500 index as a benchmark.
- A beta of 1.0 describes a stock that is perfectly correlated with the S&P 500. Values higher than 1.0 describe stocks that are more volatile than the S&P 500, while lower values describe stocks that are less volatile.
Inverse Correlation
- An inverse (or negative) correlation is when two variables in a data set are related such that when one is high the other is low.
- Even though two variables may have a strong negative correlation, this does not necessarily imply that the behavior of one has any causal influence on the other.
- The relationship between two variables can change over time and may have periods of positive correlation as well.








No comments:
Post a Comment